Pacemaker
Have an improved heart rate by balancing the pace of heartbeats with a pacemaker. Live a life free from cardiac issues.
Pacemaker implantation is a surgical process carried out by an expert cardiac surgeon when the intrinsic electrical system of your heart fails. There are different types of pacemakers based on the exact heart condition that is implanted differently. It can be both temporary and permanent.
Let’s know more about the device. It is essential to know the details if you require a pacemaker.
Functioning of a pacemaker
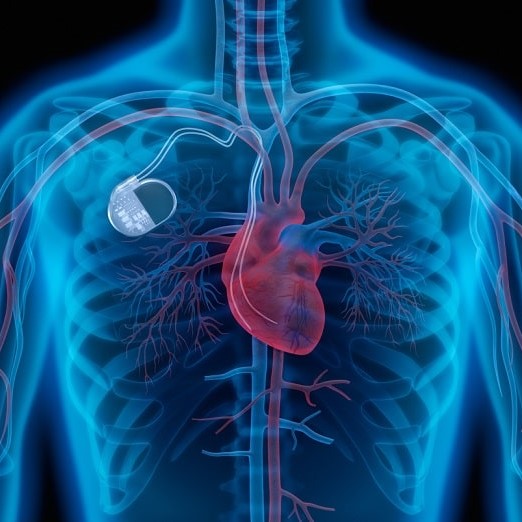
- Pulse generator: It is a small metal container with a battery and an electrical circuit that controls the rate of electrical pulses.
- Leads or electrodes: one or more insulated and flexible wires that are placed in one or more heart chambers. They deliver the electrical pulses to the heart adjusting the heart rate.
Pacemakers function only in times of need. In the case of a slower heartbeat, it will send electrical signals to the heart to regulate your beat. There are newer pacemakers that come with sensors to detect body motion or rate of breathing, helping the device detect the boost in heart rate much easier.
Types of Pacemakers
Single Chamber Pacemaker
Referring to your symptoms and the level of pace you need, the lead may also be connected to your right atrium or upper heart chamber to promote pacing.
Dual Chamber Pacemaker
Biventricular Pacemaker
If you have had heart failure, your right and left ventricle will fail to pump in rhythm. So, to program the contractions of both the ventricles at the same time, cardiologists implant CRT-D. Bringing the ventricular contractions in coordination helps the heart to pump blood efficiently and treat heart failure symptoms.
Pacemaker implantation – The Process
Preparing for the surgery:
Before fixing a pacemaker, the cardiologist will give you drugs or local anesthesia to numb the treatment area during the surgery. In some cases, blood thinning medicines are prescribed to prevent blood clots and antibiotics for infection during the process.
During the surgery:
More than one insulated, flexible wire is inserted into a vein close to or under your collarbone. The wires are guided to the heart with help of X-ray images. One end of the wire is secured to the exact location in the heart, while the other end is connected to the pulse generator of the pacemaker that is implanted under the skin below your collarbone.
After the procedure
Pacemakers can be tracked remotely. Your doctor’s office will receive the transmissions from the pacemaker that suggests your heart rhythm and rate. They will know if the device is working well and how long will its battery last.
- After discharge, do not drive back home on your own.
- Considering your heart condition, your cardiac specialist may advise you to ignore vigorous exercise or weight-lifting for at least a month or two.
- Do not apply pressure on the operated area. In case of pain or swelling, contact your doctor immediately.
In case you go for any medical tests, let the concerned doctor know about your pacemaker implantation.
Let’s start a conversation…
We understand the importance of listening.
Feel free to contact us
